In recent years, the realm of immunotherapy has experienced tremendous advancements, thanks to pioneering research and innovative methodologies. A remarkable breakthrough has emerged from Heidelberg University, where a multidisciplinary team from the Institute of Organic Chemistry and the Institute of Pharmacy and Molecular Biotechnology has successfully developed a novel chemical process. This innovation enables the rapid and efficient synthesis of modified peptides integrated with boronic acids, opening the door to exciting new possibilities in synthetic immunology.
At the core of biological systems, peptides—chains of two or more amino acids—play a critical role in various physiological processes. Particularly, they are key players in the immune system, functioning as carriers of vital immunological signals that help the body recognize pathogens. The specific arrangement and make-up of these peptides determine the body’s immune responses, effectively signaling what is foreign and necessitating a defensive action. This intrinsic connection makes peptides an invaluable resource for therapeutic and preventive strategies, acting as the basis for certain immunizations and targeting the body’s immune mechanisms.
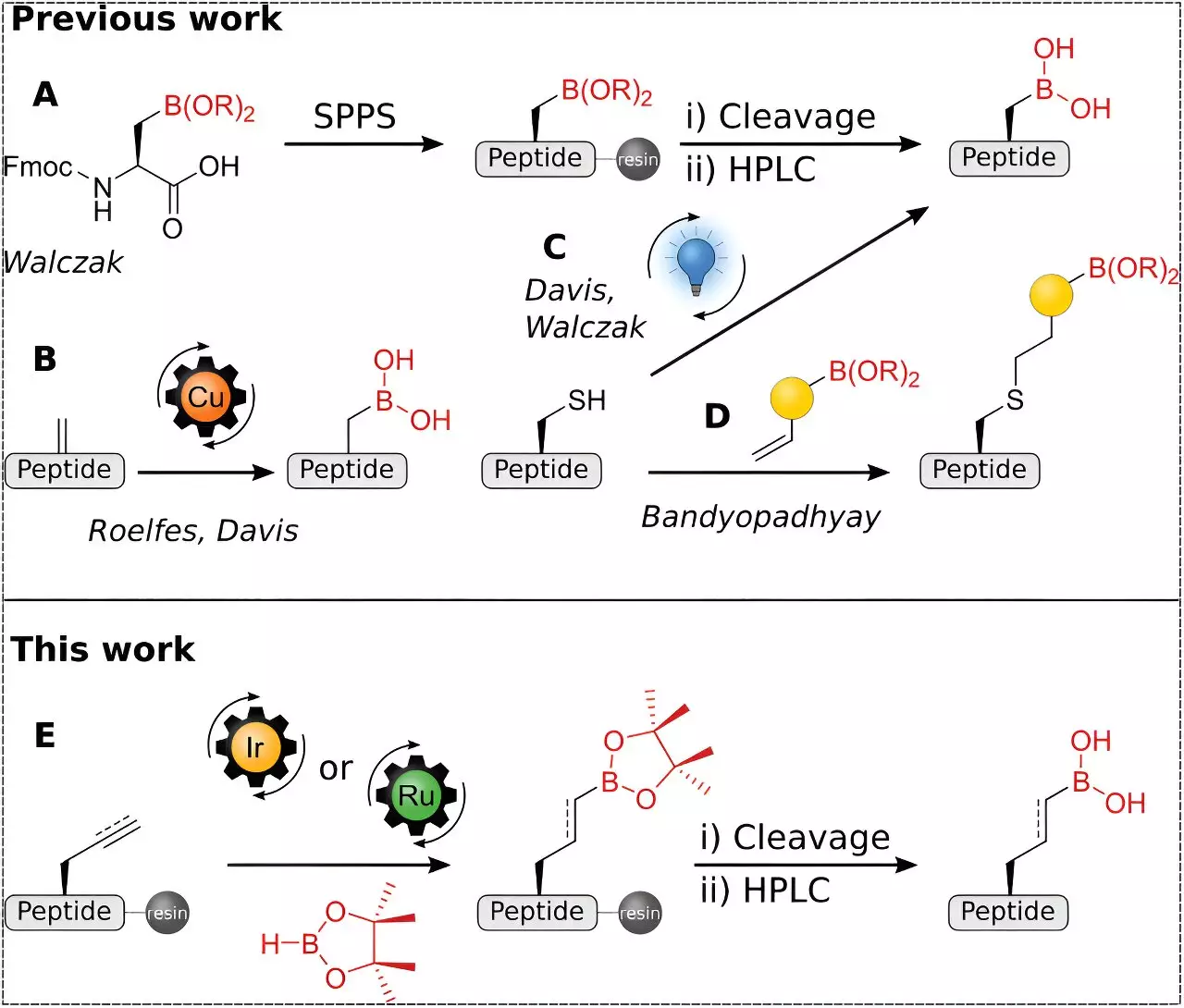
Researchers at Heidelberg University have described their latest findings in the prestigious journal, *Advanced Science*. The team was able to develop a method that incorporates boronic acids into peptides through a hydroboration process on peptide alkenes and alkynes bound to resin. This synthesis technique yields a chemical structure that was previously either challenging or impossible to achieve. The introduction of boronic acids into peptide structures is particularly compelling due to their sophisticated interaction with biological molecules, notably immune cells.
Junior Professor Dr. Franziska Thomas, who spearheaded the research, emphasizes that the incorporation of boronic acids facilitates the introduction of diverse chemical modifications within these peptides. This flexibility in design is integral, as it allows researchers to create numerous variants tailored to specific biological targets, potentially revolutionizing therapeutic strategies in immunology.
The implications of this research are vast. As stated by Prof. Dr. Christian Klein, the utility of peptide boronic acids in immunotherapeutics could lead to the development of novel treatments aimed at stimulating immune responses to combat malignancies, such as tumors. By harnessing the body’s natural defenses, it could be possible to create a methodology that effectively eradicates cancer cells, representing a promising avenue in oncology.
Moreover, the unique properties of boronic acids could also be leveraged for targeted drug delivery systems. As an “anchor” molecule, boronic acids enable peptides to attach to nanoparticles designed to transport therapeutic agents. This innovative mechanism holds the potential for controlled and localized delivery of drugs within specific organs or to particular immune cells, enhancing the efficacy of treatment while minimizing systemic side effects.
Despite the substantial progress made within this study, the journey towards realizing the therapeutic potential of peptide boronic acids is just beginning. Ongoing research will undoubtedly seek to better understand the intricate interactions between these modified peptides and immune mechanisms. This could open avenues for the development of implantable systems that dissolve within the body, strategically releasing active compounds as needed.
The foundational work performed by the Heidelberg research team not only sets the stage for future explorations into synthetic immunology but also lays the groundwork for addressing some of the most pressing challenges in modern medicine. This novel approach to peptide modification could reshape therapeutic landscapes, advancing our capabilities in treating a variety of diseases with previously unimaginable precision.
The synthesis of peptide boronic acids marks a transformative step in immunotherapy and synthetic biology. By integrating unique chemical properties with biological relevance, researchers are poised to make significant strides in the field of drug delivery and disease treatment. The combined expertise of chemists and biologists will be paramount to maximizing the potential of this groundbreaking research and honing new strategies to combat diseases effectively. The future of immunology looks promising, with peptide boronic acids at the forefront of innovation.