Lithium-ion batteries have become an integral part of modern technology, powering everything from smartphones to electric vehicles. However, they come with significant safety risks associated with their highly flammable liquid electrolytes. Researchers at Martin Luther University Halle-Wittenberg (MLU) have made a promising advancement by developing a new gel electrolyte designed to enhance the performance and safety of lithium-ion batteries. This innovative gel technology not only aims to prevent leaks of the flammable materials but also seeks to improve battery longevity and efficiency.
One of the primary issues surrounding lithium-ion batteries has been the volatility of liquid electrolytes. While these electrolytes are effective in facilitating the movement of ions between the electrodes, they pose a fire hazard if the battery is damaged, leading to potential explosions. Professor Wolfgang Binder and his team at MLU have acknowledged these challenges, emphasizing the urgent need for more secure alternatives in battery technology. Conventional methods have relied heavily on liquid electrolytes and their inherent risk factors, creating a demand for innovative solutions that can mitigate these dangers while maintaining performance.
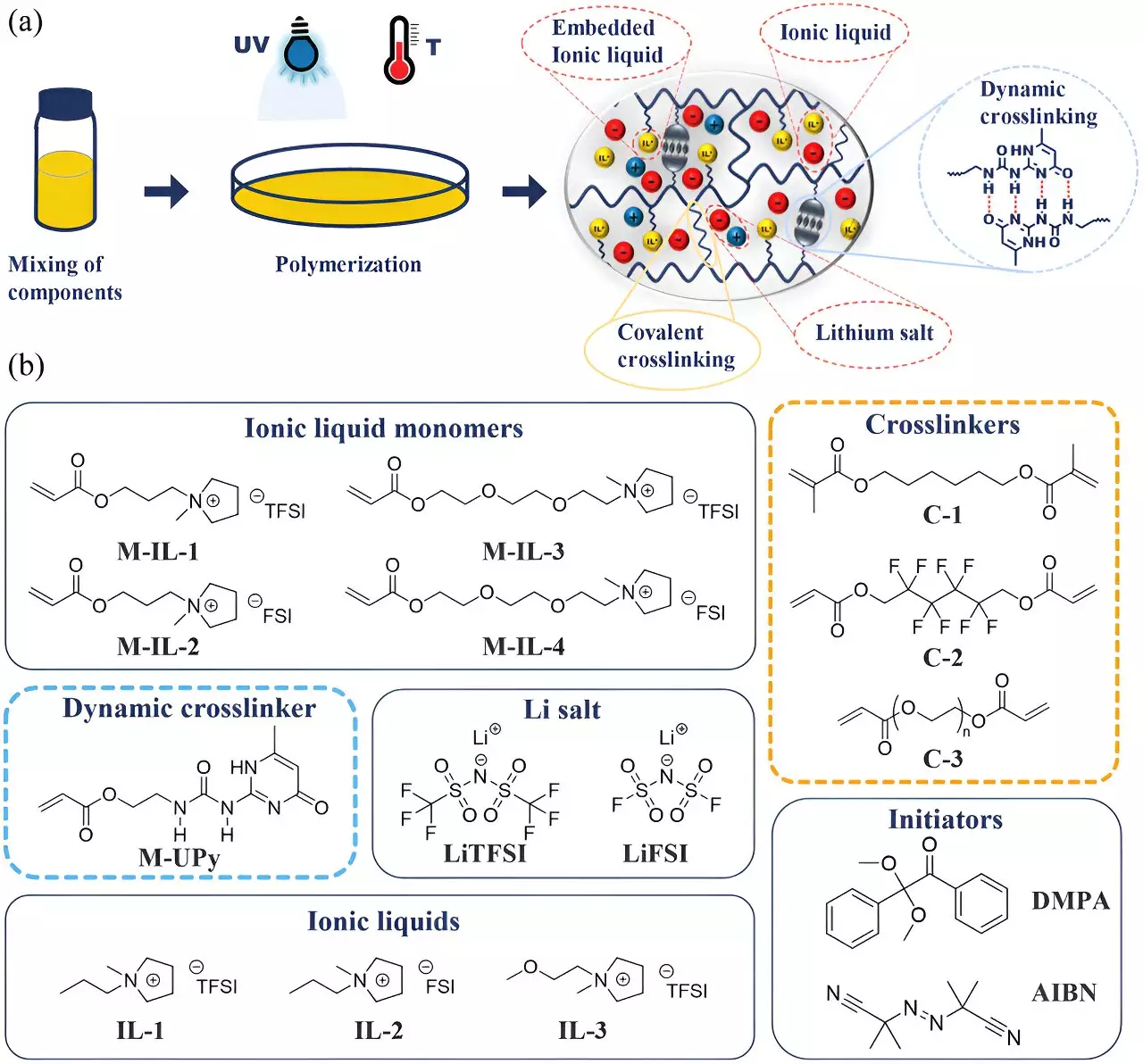
The MLU researchers have introduced a groundbreaking approach by incorporating a polymer that can fill the battery cell while binding the electrolyte in a gel-like consistency. Dr. Anja Marinow, a key figure in the research, explains that while the ions are allowed to circulate freely between electrodes, the gel provides a safeguard against leaking. This dual-functionality combines the benefits of high ionic conductivity typical of liquids with the durability and thermal stability associated with solid polymers. By doing so, the new gel electrolyte is poised to revolutionize the way energy storage is approached and utilized in various applications.
Traditional lithium-ion batteries typically operate within a voltage range that creates stability issues for liquid electrolytes, ceasing to perform effectively beyond certain critical points. The researchers at MLU have made significant strides by designing their gel electrolytes to remain stable at voltages exceeding 5 volts—an extraordinary enhancement over the standard stability threshold of around 3.6 volts for conventional cells. This remarkable improvement not only boosts performance but also reinforces safety, paving the way for advancements in battery design that could meet the demands of the modern energy landscape.
The implications of this research extend beyond mere performance enhancements; sustainability is also at the forefront of the researchers’ objectives. As the world increasingly shifts toward environmentally conscious practices, the ability to recycle these gels is an essential feature. The goal is to create batteries that can be efficiently dismantled and reused at the end of their lifecycle. Furthermore, this aligns with broader initiatives aimed at fostering a circular economy, ensuring that materials are repurposed rather than discarded.
The development of this gel electrolyte is part of a larger collaborative effort encapsulated in the “BAT4EVER” project, which unites universities and research institutions from multiple countries. The project’s collaborative nature emphasizes the significance of collective innovation in addressing global energy challenges. As research continues, the establishment of the “European Center for Just Transition Research and Impact-Driven Transfer” at MLU will serve as a hub for the ongoing exploration of sustainable technologies, setting the stage for future breakthroughs in energy storage.
The work accomplished by the researchers at MLU represents a pivotal moment in the evolution of lithium-ion battery technology. With the introduction of a gel electrolyte that enhances safety, performance, and sustainability, the future of battery technology appears brighter. While further long-term studies and industrial applications are still on the horizon, the foundation laid by this research promises to propel the entire industry towards safer and more efficient energy practices. As society continues to rely heavily on portable and renewable energy sources, innovations like these will undoubtedly shape the future of technology and sustainable living.