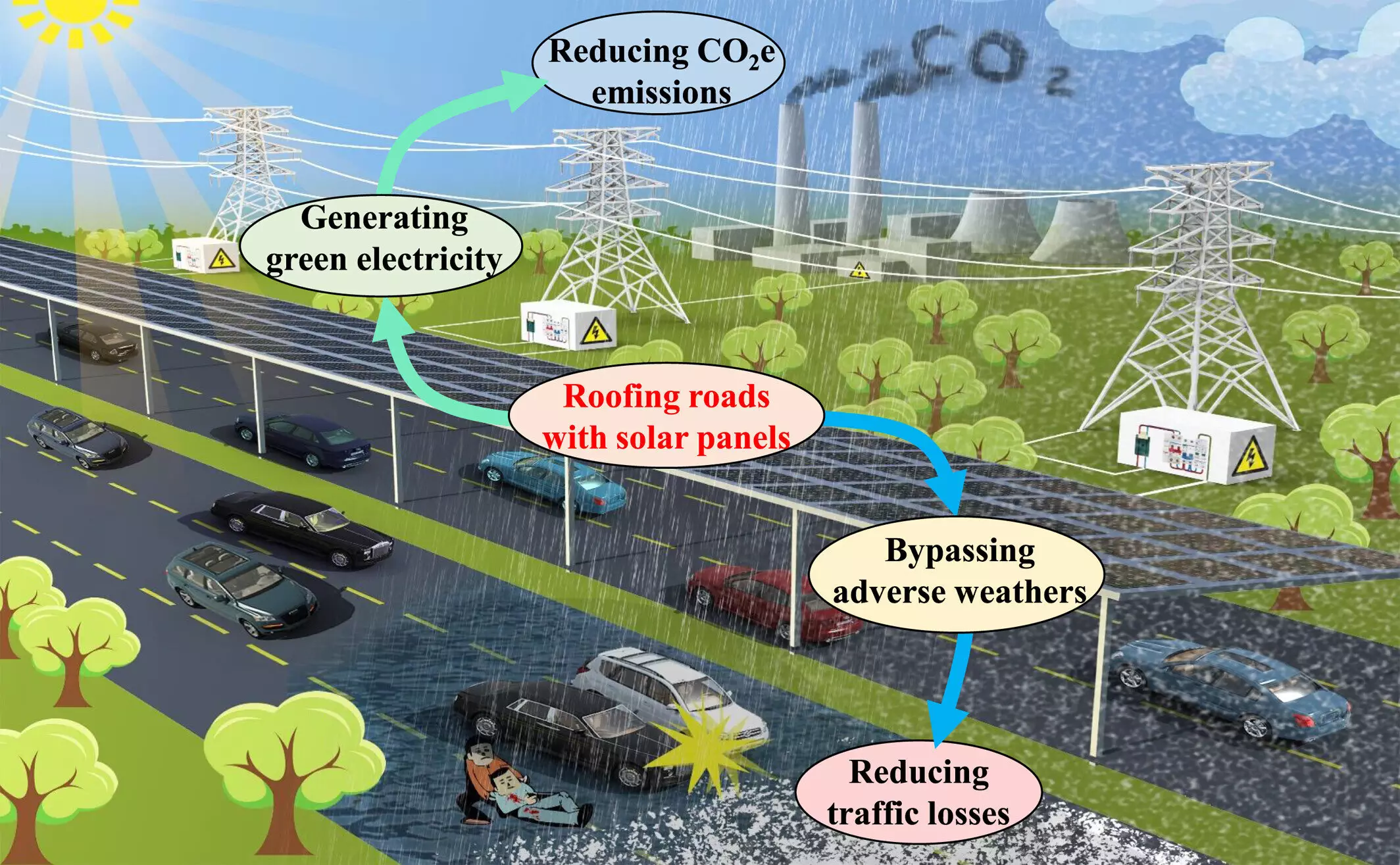
The urgent need for innovative solutions to mitigate climate change has never been more critical. Recent research suggests an ambitious plan that could reshape our approach to renewable energy: covering highways across the globe with solar panel canopies. This revolutionary idea has the potential to cut carbon dioxide emissions significantly, possibly by up to 28%, simply by reducing reliance on fossil fuels. With the new infrastructure, highways could become more than just roads; they would transform into vital sources of sustainable energy.
The research, published in the esteemed journal Earth’s Future, highlights the potential of this concept and presents a startling estimate that solar-covered highways could generate an astonishing 17.58 petawatt hours of electricity annually. This output could satisfy over 60% of the world’s electricity consumption in 2023, representing a paradigm shift in how we harness energy from existing resources.
Conceptualizing the Future of Transport
The vision for extending solar technology over our highways originated from a moment of inspiration experienced by the study’s lead author, Ling Yao, during a routine commute. Gazing down from an overpass, Yao contemplated the interconnectedness of roads and vehicles, musings transformed into a visionary idea to utilize these structures as networks of energy generation. The proposal encapsulates a brilliant blend of practicality and innovation, using already developed land to generate renewable energy and reduce greenhouse gas emissions simultaneously.
According to the data, there are over 3.2 million kilometers (1.9 million miles) of highways globally, forming a near-endless canvas for potential solar energy harvesting. Although solar-paneled parking lots have seen increased implementation, the concept of integrating solar panels directly into road infrastructures remains largely unexplored. The potential for conversion is monumental, yet effective large-scale implementations are still dauntingly absent.
The initial stages of this concept require significant financial investment and careful planning. The study conducted an analysis based on the estimated costs for both construction and ongoing maintenance of these solar roofs. Research indicates that around 52.3 billion solar panels would be required for a global project of this magnitude. These calculations were grounded in the use of polysilicon photovoltaic panels that possess a maximum generation capacity of 250 watts, strategically tilted for optimized energy production.
Geographical variability in energy generation potential and installation costs must be addressed. Areas densely populated with highway networks—such as eastern China, western Europe, and the U.S. East Coast—would likely be the most advantageous for these solar arrays. While the upfront costs may be significant—potentially reaching four times that of ground-based systems—the long-term benefits could outweigh these initial expenditures. The capability of this solar infrastructure to replace approximately 9.66 gigatons of CO2 emissions annually could provide a powerful incentive for governments and industries to consider these investments seriously.
Interestingly, the proposed solar roofs are not just an environmental safeguard; they may also enhance roadway safety. The research indicates that the presence of solar canopies could reduce traffic fatalities by 10.8%. This safety improvement can be attributed to the shields provided by the solar roofs against adverse weather conditions such as rain and snow, which can compromise driving safety. Moreover, reducing accidents not only saves lives but also curtails the economic costs associated with traffic incidents, presenting a compelling argument for broader implementation of this innovative system.
Challenges and the Need for Pilot Programs
Despite the overwhelming benefits, the ambitious project faces various challenges. Among them are the costs involved in setting up and maintaining vast arrays of solar panels. Moreover, logistical issues, such as how to clean the extensive installation without disrupting traffic flow, require consideration and planning.
However, Yao and his colleagues remain optimistic that successful pilot programs can pave the way for larger-scale implementations. They envision that stretches of flat highways, particularly in arid regions like the southwestern United States, present ideal conditions for solar construction. Ultimately, the realization of solar-powered highways could stand as a testament to human ingenuity and resilience in combating climate change.
The vision of solar-roofed highways embodies the intersection of mobility, safety, and sustainability. By repurposing existing infrastructure, we have the opportunity to create a world where travel not only supports our daily lives but also actively contributes to a cleaner environment. The road ahead is filled with challenges, yet the potential rewards of reduced emissions, safer travel, and a sustainable energy future are too significant to ignore. As global citizens, we must champion these ideas, turning bold concepts into reality for generations to come.