Access to clean drinking water is an intrinsic human right, yet the stark reality is that billions still struggle to obtain it. As the global population surges, the quest for accessible, safe drinking water has become increasingly daunting. With industrial activities and urban development exacerbating water contamination, the push towards innovative purification technologies is no longer a luxury—it’s a necessity. Traditional water treatment methods often cast a wide net, removing various ions but lacking specificity. This broad approach results in the loss of beneficial minerals alongside harmful substances, complicating our water crisis even further. A recent study by the HeKKSaGOn Alliance, comprising scientists from Kyoto, Osaka, and Heidelberg Universities, shines light on a revolutionary solution rooted in nature itself.
The Power of Phytochelatin
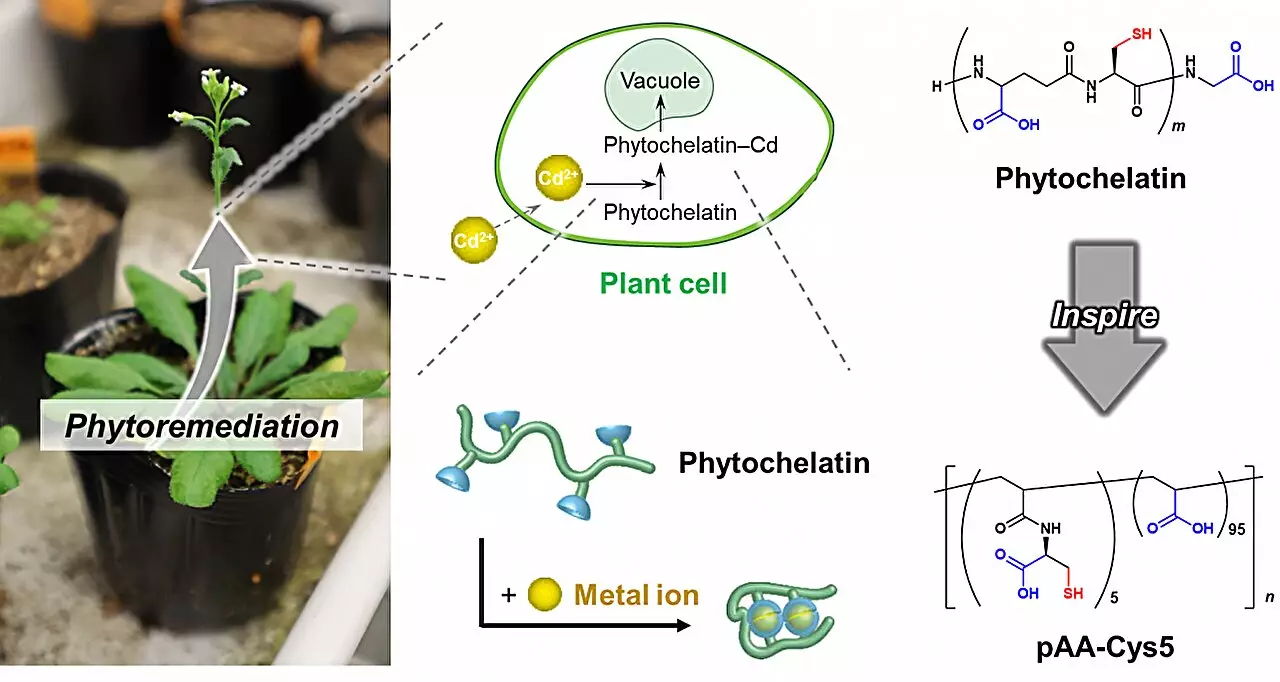
At the heart of this research is phytochelatin—an extraordinary protein that plants utilize to navigate the treacherous landscape of heavy metal toxicity. This protein not only binds specifically to harmful ions such as cadmium but also facilitates their seclusion within plant cells, preventing them from wreaking havoc. The research team embarked on a quest to unveil phytochelatin’s secrets, focusing on its molecular structure to understand how it exhibits selectivity. The identification of two critical groups—carboxylate and thiolate—formed the basis for developing a synthetic polymer, laying the groundwork for a new chapter in water purification technology.
A Synthetic Marvel: The Polymer’s Mechanism
Equipped with a keen understanding of phytochelatin’s binding properties, the researchers crafted a polymer anchored to silica beads and cellulose membranes. This design concentrated the polymer, allowing it to work within a minuscule volume—an approach that led to astonishing efficiency. The study revealed that by flowing contaminated water past the innovative polymer, the team achieved a remarkable feat: it removed cadmium ions effectively, bringing water down to safe drinking standards within a mere hour. What’s inspiring about this polymer is its specificity, effectively distinguishing and targeting cadmium while sparing essential ions like magnesium and calcium.
The Potential Beyond Cadmium
The implications of this research extend well beyond cadmium alone. The polymer’s capacity to bind with mercury ions suggests that it could serve as a versatile tool for removing a variety of heavy metals from water supplies. This multilayered approach not only holds promise for immediate applications but also opens avenues for comprehensive water treatment solutions that prioritize health without sacrificing efficiency.
Nature as a Blueprint
What makes this scientific breakthrough truly remarkable is the intersection of nature and technology. The journey began with a profound understanding of biology’s intricate mechanisms, followed by the human ability to replicate and innovate. The lead researcher, Masaki Nakahata, expressed excitement over how their synthetic polymer even surpasses the natural efficiency of plant proteins. This type of biomimicry illustrates an essential lesson: nature often holds the key to solving our most pressing problems. Instead of placing technology in opposition to the environment, the study champions a future where human ingenuity harmonizes with ecological wisdom.
Looking Ahead: Unleashing the Polymer’s Full Potential
The road ahead is filled with opportunities for further exploration. While the polymer shows promise, its application on a larger scale requires additional research and fine-tuning, particularly in real-world settings. This study is a stepping stone towards innovative water treatment technologies that can potentially revolutionize how we perceive and manage our water resources.
In a world increasingly threatened by pollution and depletion, the fusion of scientific insight and natural mechanisms illuminates the path forward. The challenge now is translating this remarkable discovery into practical solutions that can be deployed in underserved communities globally. The intersection of science, sustainability, and ethics will be essential in ensuring that clean water becomes a reality for everyone. This remarkable breakthrough represents not just an advancement in technology but a renewed hope for the countless individuals battling against the water crisis every day.