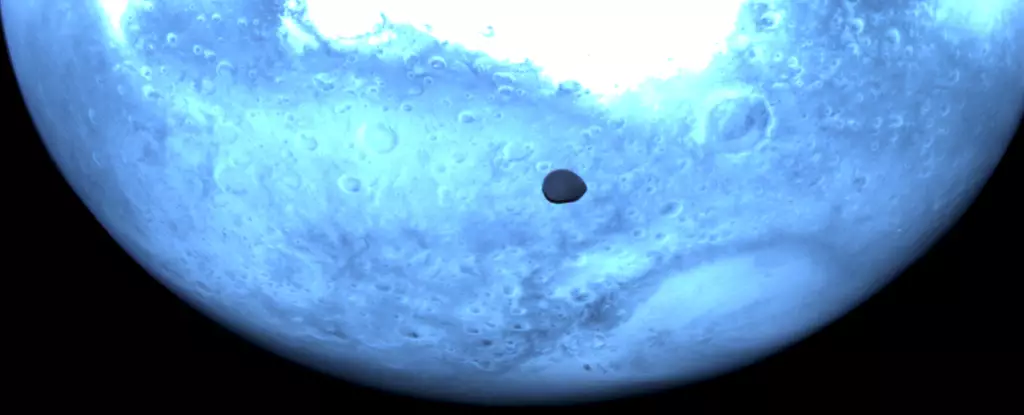
In an extraordinary endeavor, the European Space Agency’s HERA mission is poised to redefine the boundaries of our understanding of asteroid impacts and planetary defense techniques. Recently, HERA captured breathtaking images of Mars’ enigmatic moon, Deimos, during its gravitational slingshot around the Red Planet, a vital maneuver on its ambitious journey to study the asteroid Dimorphos. Scheduled to reach its target in late 2026, HERA is not merely a mission of exploration; it carries the weight of potential planetary defense against world-threatening asteroids. The stakes have never been higher, and initiatives like HERA are essential as humanity confronts the celestial forces that could alter life on Earth as we know it.
Deimos: A Puzzle in the Cosmos
Among the most fascinating results of the HERA mission’s close pass by Mars are the newfound images of Deimos. This small and lumpy moon, measuring a mere 12.5 kilometers in diameter, remains one of the more perplexing subjects in astronomy. Although less famous than its larger counterpart, Phobos, Deimos has captured the attention of scientists demanding answers about its origins. Theories abound: were they once rogue asteroids drawn into orbit by Mars’ gravitational field, or did they originate from colossal impacts on the Martian surface? Each scenario presents tantalizing implications, and HERA’s images add critical data, piecing together our understanding of planetary formation and solar system dynamics.
The Role of Technology in Space Exploration
The significance of HERA’s mission lies not just in the destination but in the scientific tools that accompany it. Utilizing advanced imaging technologies, including the innovative “HyperScout” and thermal infrared imagers, HERA offers a glimpse into the Martian moon’s make-up, revealing colors and features invisible to the naked eye. The strange blue hue of some images, attributed to the infrared capabilities, underscores the cutting-edge advancements in space exploration that make this mission possible. These technological feats are not mere novelties; they are essential for unraveling the mysteries held by our solar neighbors.
The Implications of Dimorphos Study
While the flyby yielded insightful images of Deimos, HERA’s core mission revolves around understanding Dimorphos, an asteroid that has recently come under scrutiny following NASA’s DART mission, which successfully altered its orbit. This groundbreaking test of planetary defense protocols showcased a feasible route for mitigating asteroid threats—a prospect that transforms the narrative around potential cosmic collisions. Earth faces a spectrum of risks from asteroids, and the study of Dimorphos serves as an early blueprint for humanity’s response capabilities.
By analyzing how effectively DART changed Dimorphos’ orbit, mission scientists aim to evaluate if such impact techniques could become instrumental in diverting asteroids on collision courses with Earth. The urgency cannot be understated, especially given the increasing awareness of astronomical bodies capable of catastrophic outcomes, as highlighted by the recent concern regarding asteroid 2024 YR.
Future Endeavors in Planetary Defense
In light of these discoveries and encounters, the European Space Agency is ramping up its efforts toward safeguarding Earth. The anticipated Ramses mission, aimed at the colossal asteroid Apophis, exemplifies the proactive measures being taken. Missing the chance to observe such formidable objects could lead to catastrophic consequences. Scheduled to approach within 32,000 kilometers of Earth in 2029, Apophis demands our attention now, while we still have the luxury of preparation. Should the ESA approval come through, it would launch in 2028, providing critical insights in time for encounters that could redefine our place in the cosmos.
The dawning of space exploration calls for vigilance and preparedness, as each discovery untangles threads of knowledge essential for our survival. The progress made by missions like HERA invigorates the dialogue about planetary defense, underlining our responsibility to harness technological advancements not just for exploration but for the safeguarding of our planet. As humanity reaches farther into the void, we must be ready to confront the threats lurking within it and turn them into opportunities for unity and innovation.