In recent scientific revelations, a disturbing picture has emerged regarding the safety of vaping, especially for pregnant women. A groundbreaking study conducted by researchers at Ohio State University uncovered that even exposure to the most basic components of vape liquids—without any added nicotine or artificial flavorings—can negatively impact fetal development. Specifically, the research demonstrated that the offspring of exposed mice were born with noticeably smaller and narrower skulls, a change that echoes some developmental anomalies observed in human children. This finding should prompt us to reconsider assumptions about the harmlessness of nicotine-free vaping products.
What makes this discovery particularly alarming is that the experimental vapor only contained common carrier substances—propylene glycol and glycerol—former staples in vaping formulations. These substances are typically considered inert, safe, or at worst, benign. Yet, the study’s revelations challenge this narrative, suggesting that even these components, in isolation, may carry unforeseen risks during sensitive developmental periods like pregnancy.
The implications are far-reaching. Pregnant women often turn to vaping as a supposedly safer alternative to smoking, convinced that removing nicotine and flavorings eliminates health risks. However, this study urges us to scrutinize that belief. If the very base ingredients of vape fluids can alter fetal skull growth, then the perceived safety of nicotine-free vapes warrants serious doubt. As we navigate an era of widespread vaping, this evidence underscores the importance of exercising caution, particularly for those carrying life within them.
Decoding the Role of Core Vape Components: Are They Truly Safe?
Understanding the precise impact of vape ingredients requires dissecting their individual effects. Propylene glycol and glycerol—the main carriers in most vape liquids—are generally regarded as safe in food and pharmaceutical applications. Nonetheless, their behavior when inhaled, especially over prolonged periods or during pregnancy, remains insufficiently studied.
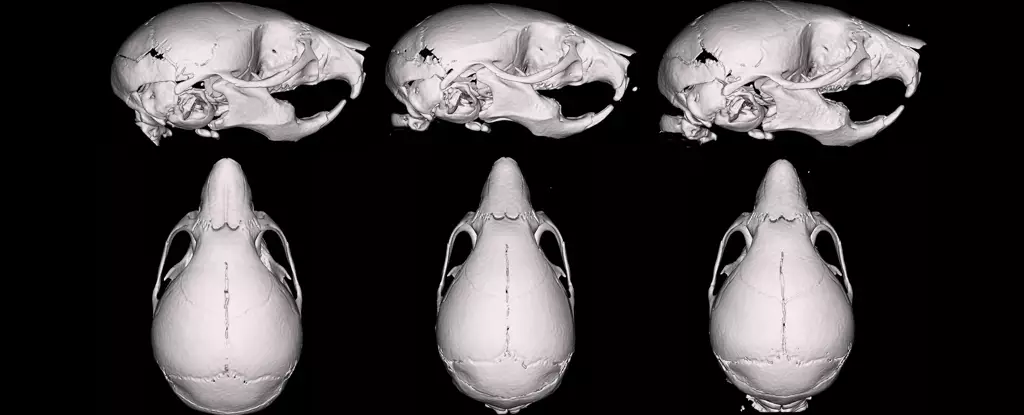
The study employed two formulations: a 50/50 mix and a 30/70 glycerol-rich blend. Interestingly, the outcomes defied expectations. Researchers hypothesized that the formula with more propylene glycol, known for increasing nicotine absorption, would have a greater adverse impact. Instead, it was the more glycerol-dominant mixture that resulted in more pronounced morphological changes in the pups, including smaller cranial structures and narrower faces.
This counterintuitive result raises profound questions about our assumptions regarding safety and component interactions. Could the increased glycerol content be forming other compounds when vaporized? Might these breakdown products be more biologically active or risky? Furthermore, the reduction in pup weight, even within normal ranges, hints at altered development that could carry longer-term consequences. This leads us to a critical insight: the common belief that carrier substances are inert needs challenging, especially in vulnerable populations like pregnant females.
The broader lesson here is the importance of scientific nuance. Simplistic ideas—such as “only nicotine is harmful”—miss the complex chemistry underlying inhaled substances. Policymakers, health professionals, and consumers alike should demand scrutiny of even seemingly benign ingredients.
From Animal Models to Human Realities: The Complex Path to Understanding Vaping Risks
Animal studies often serve as a vital bridge in scientific inquiry, offering insights impossible to glean through direct human experimentation. However, translating these findings into concrete warnings for humans remains complex. Mice, with their relatively short gestation periods and biological differences, provide valuable clues but not definitive answers.
Cray and his team’s research reminds us that vaping’s impact isn’t just about the chemical composition; it’s also about exposure patterns, individual susceptibilities, and developmental stages. The experimental exposure—one puff per minute over several hours daily—mirrors heavy vaping habits but doesn’t precisely replicate human use. Still, the observation that even the simplest formulations can alter skull dimensions raises serious concerns about the unseen effects of vaping during pregnancy.
Additionally, the variability in actual vape products complicates the picture. Many commercial e-cigarettes and liquids contain a cocktail of chemicals, flavorings, and additives, some of which can produce new compounds when heated. The lack of regulation and comprehensive labeling exacerbates uncertainty, meaning consumers are often navigating a fog of unknowns.
Regulatory agencies must step up to bridge this knowledge gap. Isolating the effects of individual components—as in this study—is an essential strategy, but real-world vaping involves complex mixtures and heating mechanisms that can produce hazardous byproducts. Therefore, the call for stricter oversight, better labeling, and ongoing research is urgent if we are to protect vulnerable populations.
Reevaluating Vaping’s Perceived Safety: A Wake-Up Call for Expectant Mothers
Vaping has long been promoted as a safer alternative for smokers seeking to quit, with the added allure of fewer toxins and perceived health benefits. However, the emerging evidence suggests that this narrative is overly simplistic and dangerously misleading, especially for pregnant women.
The notion that nicotine-free vapes are harmless is now challenged by findings indicating that their base components—propylene glycol and glycerol—may interfere with fetal development in ways previously unimagined. This doesn’t just challenge individual choices but also impacts public health messaging and regulatory policies.
For women who are pregnant or planning pregnancy, the message should be clear: vaping isn’t a risk-free activity. The developmental alterations observed in animal models hint at similar vulnerabilities in humans, such as altered skull shape, facial structure, and potentially other neurodevelopmental issues. These findings could have lifelong consequences, affecting not just physical appearance but cognitive and sensory functions as well.
Ultimately, the responsibility falls on regulators, healthcare providers, and public health advocates to conduct comprehensive studies, raise awareness about these risks, and encourage precaution rather than complacency. Until the full spectrum of vaping’s effects is understood, especially during critical periods of development like pregnancy, it’s prudent to err on the side of caution. The allure of “safer” vaping options masks a complex chemistry that can silently undermine developmental health—an alarm that demands our immediate attention and unwavering vigilance.